What is Kosher
What is Kosher
The definition of Kosher is a food that is considered clean or fit to eat by Jewish dietary laws, or is slang for OK or CORRECT. It’s the food that satisfies the requirement of Jewish law. A food product or beverage can apply the kosher label if each ingredient used therein, food additives, colorants, preservatives, process, equipment’sand methods are fully compliant with Kosher specifications.Rabbi finally approved the production process before the any organization can apply the Kosher logo. Kosher Laws are so strict that if equipment’s used to manufacture any non-kosher foods or item are used for kosher foods then that specific food can no longer carry the kosher label until cleaning is not done as per Kosher standards.
Pareve
Food not carrying of dairy or meat components is termed Pareve. Fruits, vegetables, grains, fish and eggs are considered eligible for Pareve label. Fruits and vegetables must be washed thoroughly to remove any lurking insects.
For foods to carry the pareve label, care must be taken that they are not processed in equipment’s that are used to process dairy or meat products at temperatures above 40 deg. C.
Although fish is considered kosher but all fishes are not kosher ,Only fish species that have fins and scales that can be removed with ease are considered kosher. Tuna, sole, plaice and salmon are kosher. Shellfish, eels, shark, monkfish, huss, catfish and sturgeon are non-kosher. Fish by products such as roe and fish oil as well as gelatine are certified kosher only if derived from kosher fish.
Similar Eggs are kosher provided they are obtained from kosher birds and do not carry any blood spots.

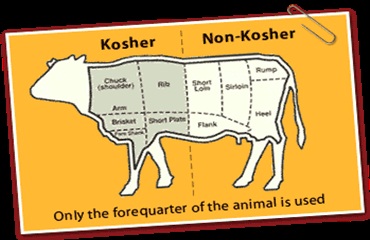
Only specific animals and birds are considered kosher according to the Bible. Buffalo, Goats and Sheep are kosher. Chicken, turkey, goose and duck are kosher. Slaughter of animals and birds must follow Jewish laws. Blood needs to be removed by salting or roasting process and this process of slaughter and salting is supervised by a rabbi.

Any Dairy products can carry the kosher label only if milk is obtained from kosher animals. Strictly orthodox communities may specify strict supervision which is known as Cholov Yisroel, which is particularly implemented in the manufacture of cheese in which rennet derived from animal intestines or stomach is used.

Grape juice, wine vinegar and wine made using dried or fresh grapes requires handling by Jews from start to finish in order to qualify for the Kosher label. Any product that uses grape flavoring or grape additives requires kosher certification.

Bread can carry kosher at two levels. Bread or similar products must also comply with regular kosher norms in addition to the two levels. These two levels are Pas Palter meaning bread made by a non-Jewish professional baker and Pas Yisroel meaning bread prepared and baked by Jews in accordance with age old Jewish methods. Orthodox Jews would insist on Pas Yisroel while others would find Pas Palter acceptable.

All insects are non-kosher and specific care must be taken to ensure vegetables and fruits are free of insects by thorough washing, cleaning and inspection for such category of foods to qualify for kosher label.

The Jews celebrate Passover for 8 days during springtime and during this period it is expressly forbidden to partake of fermented food or beverages made using barley, oat, spelt, rye and wheat. Even utensils used for preparing foods or cooking foods using these ingredients is forbidden during Passover.
